Einstein Discovery (ED) is a powerful AI-driven analytics tool designed to help users uncover meaningful insights and make accurate predictions from their data—without the need to build complex machine learning models manually. While ED excels at generating sophisticated models, the quality of its output heavily depends on the quality of the input data. In other words: garbage in, garbage out. That’s why preparing clean, well-structured data is a critical step in the process.
Data preparation involves understanding your dataset thoroughly—identifying which columns are irrelevant, which ones need transformation, and how to structure the data to best support your predictive goals.
Why Data Prep Recipes Matter for Einstein Discovery
Einstein Discovery is outcome-oriented. For example, if your goal is to predict customer churn, you’ll need historical data that clearly indicates which customers have churned. If this data resides in Salesforce, you’re in luck—CRM Analytics integrates seamlessly with Salesforce. If your data is stored elsewhere, CRM Analytics (formerly known as Tableau CRM) offers a variety of built-in connectors and also supports CSV file uploads for easy data import.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Data Prep Recipes
To get your data ready for ED, you’ll use a Data Prep Recipe—a versatile feature in CRM Analytics that simplifies data transformation. Recipes allow you to merge datasets, apply transformations, and prepare your data efficiently.
Each recipe begins with an input node, which pulls in data from a connected source like Salesforce or an existing dataset. From there, you can branch out using various node types depending on the operations you need to perform. These include:
- Transform – Modify columns or values
- Filter – Narrow down your dataset
- Aggregate – Summarize data
- Join – Combine datasets based on common fields
- Append – Stack datasets vertically
- Output – Save the final dataset for use in ED
With the right recipe, you can ensure your data is clean, relevant, and ready to power insightful predictions with Einstein Discovery.
Let’s explore each operation in detail.
Transform
The Transform node in CRM Analytics Recipes is one of the most versatile tools for preparing data for Einstein Discovery. It allows you to clean, restructure, and enrich your dataset by applying different functions. These transformations ensure consistency and usability, which are critical for accurate predictions.
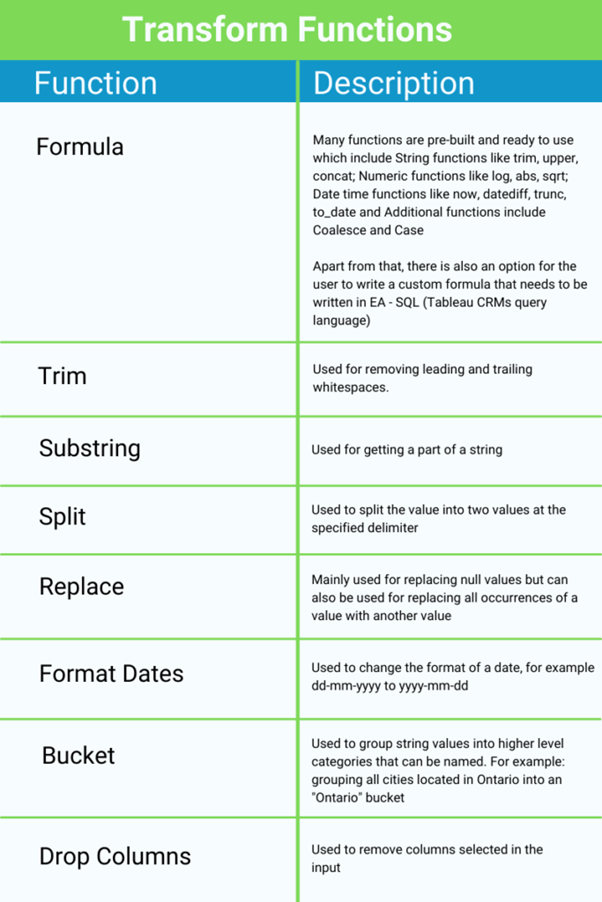
By leveraging these operations, you can ensure that your dataset is not only clean but also structured in a way that aligns perfectly with your analysis and prediction goals.
Filter
Filters help eliminate irrelevant or unwanted data, allowing you to focus only on the records that matter for your analysis. This is especially useful when working with large datasets where not all entries apply to your use case.
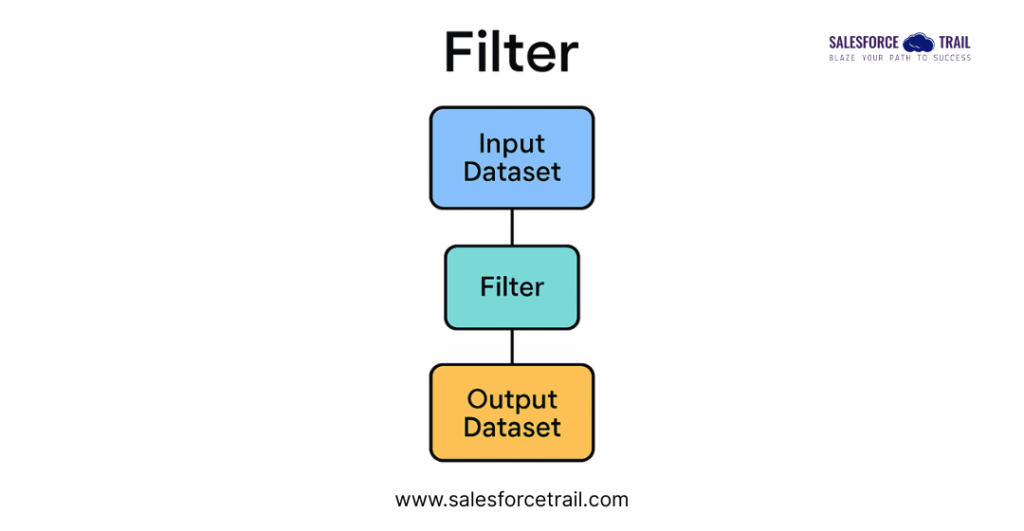
Example:
Suppose you want to analyze customer behavior starting from the year 2025. You can apply a filter to include only records where the Created Date is on or after January 1, 2025.
Filter Condition: Created Date ≥ 2025-01-01
This will remove all records created before 2025, ensuring your analysis is based on recent and relevant data.
Read More: CRM Analytics Summer ’25 Release Updates
Aggregate
The Aggregate operation is ideal for summarizing large datasets. It functions similarly to Excel’s pivot tables but offers more flexibility and power within CRM Analytics. One important thing to note: you must define at least one aggregation function—grouping without aggregation is not allowed.
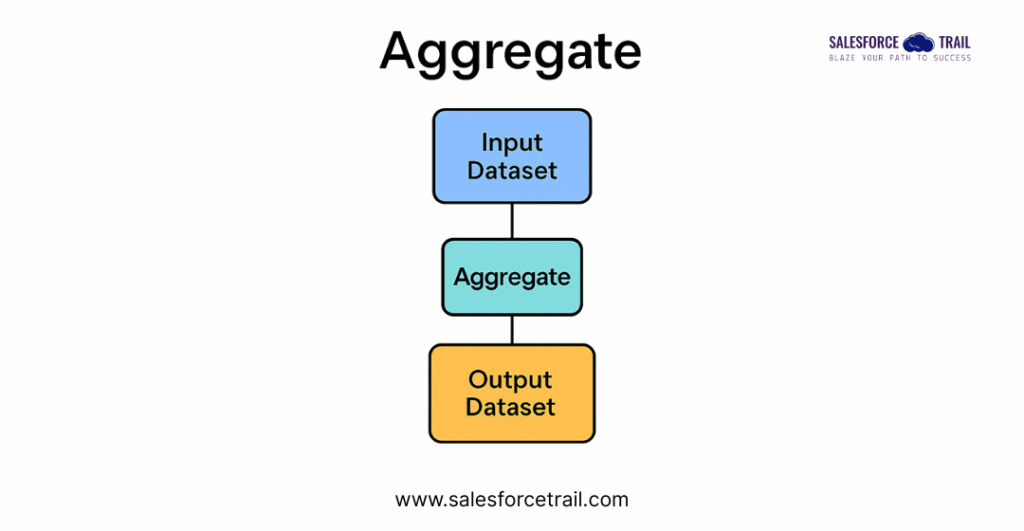
Aggregates allow you to apply formulas such as Sum, Average, Count, and more. For a full list of supported formulas, you can refer to the Salesforce documentation on Aggregate Nodes.
Example: Basic Aggregation
Let’s say you want to count how many Account records exist in each city.
- Group By: City
- Aggregate: Count(Account ID)
Hierarchical Aggregation
This advanced feature is designed for multi-level data structures. It allows you to roll up values across hierarchical relationships—like summing sales figures up a management chain—without manually calculating each level.
Example: Hierarchical Aggregation
Imagine you have sales data for individual salespeople and want to see total sales by team and director.
- Hierarchy: Salesperson → Team Lead → Director
- Aggregate: Sum(Sales Amount)
For a full breakdown, you can refer here
Join
When your data lives in multiple places, joins help unify it into a single dataset. CRM Analytics supports multiple join types:
Lookup Join
Purpose: Enrich your main dataset with a single matching value from another dataset.
Example :
You have a Sales Transactions dataset and want to add the Region from the Store Info dataset using Store ID.
- Recipe Dataset: Sales Transactions
- Join Dataset: Store Info
- Join Key: Store ID
- Result: Each transaction now includes the region of the store.
Left Join
Purpose: Keep all records from the main dataset and bring in all matching records from the joined dataset.
Example :
You have a Customer Orders dataset and want to bring in all matching Product Details.
- Recipe Dataset: Customer Orders
- Join Dataset: Product Catalog
- Join Key: Product ID
- Result: All orders are retained, even if some products have multiple entries (e.g., different versions).
Right Join
Purpose: Keep all records from the joined dataset and bring in all matching records from the main dataset.
Example :
You have a Support Tickets dataset and want to ensure all Customer Feedback entries are included, even if some tickets are missing.
- Recipe Dataset: Support Tickets
- Join Dataset: Customer Feedback
- Join Key: Ticket ID
- Result: All feedback entries are retained, even if some tickets don’t exist in the main dataset.
Inner Join
Purpose: Keep only records that exist in both datasets.
Example :
You want to analyze only those Leads that have corresponding Opportunities.
- Recipe Dataset: Leads
- Join Dataset: Opportunities
- Join Key: Lead ID
- Result: Only leads that converted into opportunities are included.
Outer Join
Purpose: Include all records from both datasets, regardless of whether they match.
Example :
You want a complete view of Employees and Project Assignments, including those who are not assigned to any project and projects with no assigned employees.
- Recipe Dataset: Employees
- Join Dataset: Project Assignments
- Join Key: Employee ID
- Result: All employees and all projects are included, matched or not.
Tip:
Choosing the right join type is crucial. For instance, a Right Join may significantly increase your dataset size compared to a Lookup or Inner Join, which are more selective.
Following is the Join operation flowchart illustrating how different join types work in CRM Analytics

Append
The Append operation is used to combine two or more datasets that have similar structures (i.e., the same or compatible columns). It’s like stacking datasets on top of each other. This is especially useful when you’re working with time-based data (e.g., quarterly reports) or data split across regions or departments.
When appending, you map fields from the recipe dataset to the selected dataset. If a column exists in one dataset but not the other, the missing values will appear as null in the final result.
Example 1: Quarterly Sales Data
You have separate datasets for Q1 and Q2 sales and want to analyze the half-year performance.
- Dataset 1: Q1_Sales
- Dataset 2: Q2_Sales
- Mapped Fields: Date, Product ID, Sales Amount
Result: A single dataset with all sales records from both quarters.
Example 2: Regional Employee Records
You maintain employee data separately for the North and South regions and want to create a unified employee directory.
- Dataset 1: North_Employees
- Dataset 2: South_Employees
- Mapped Fields: Employee ID, Name, Department, Region
Result: A consolidated dataset of all employees across both regions.
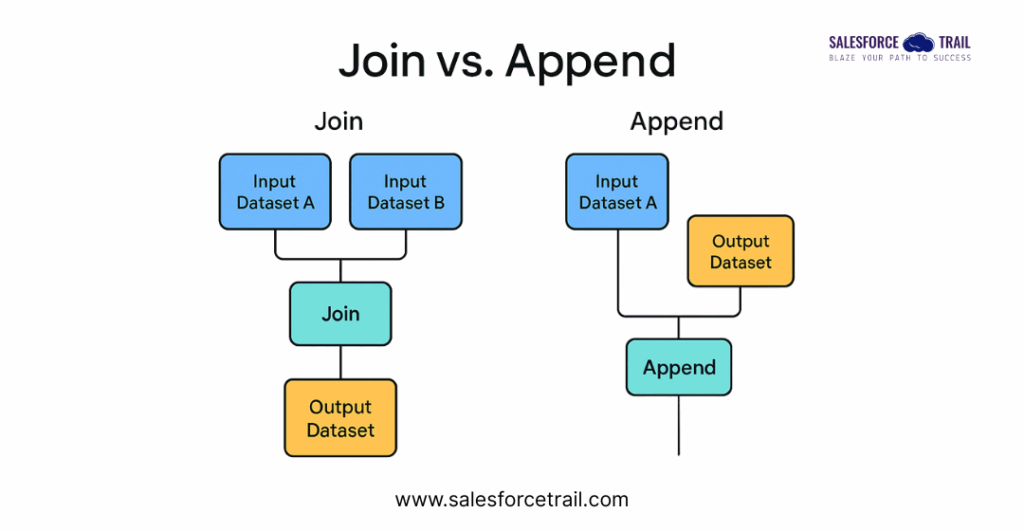
The following is the visual flowchart illustrating the differences between Join and Append operations in CRM Analytics:
Join vs Append Flowchart
Output
Finally, the Output node saves your transformed dataset:
As a dataset in CRM Analytics (recommended for Einstein Discovery)
Or as a CSV file for external use
Think of it as publishing your recipe—this dataset is now ready to fuel Einstein Discovery predictions.
Final Thoughts
This review has focused on the tools available in CRM Analytics, Dataprep Recipes, and the steps that go into creating an Einstein Discovery-ready dataset.
If you have any questions about this blog or how to leverage CRM Analytics and Einstein Discovery to solve enterprise business challenges, reach out to me.
Most Reads:
- How to Become a Salesforce Consultant: A Complete Guide to Success
- How to Become a Salesforce Solution Architect: A Complete Guide to Success
- Best Tips and Tricks to Ace Your Salesforce Interviews in 2025
- Dreamforce 2025 Registration is Open Now: Everything You Need to Know
- How to Crack the Salesforce Interview: Real Questions and Tips from Experts
Resources
- [Salesforce Developer]- (Join Now)
- [Salesforce Success Community] (https://success.salesforce.com/)
For more insights, trends, and news related to Salesforce, stay tuned with Salesforce Trail

Ganesh Ega
Ganesh brings over 4+ years of expertise in CRM Analytics, with a strong background in Salesforce development. As a seasoned software developer, he has created numerous dashboards and solutions using Salesforce CRM Analytics. His passion for staying up-to-date with the latest enhancements and features drives him to continuously master new skills. Ganesh is dedicated to sharing his knowledge and expertise with others, empowering them to unlock the full potential of CRM Analytics
- Ganesh Ega#molongui-disabled-link
- Ganesh Ega#molongui-disabled-link
- Ganesh Ega#molongui-disabled-link