AI agents built with Agentforce and Flow are reshaping how teams automate work inside Salesforce. With Flow—the platform’s powerful no-code automation tool—you can design intelligent, task-ready agents that operate securely within your org and adapt to real business processes. These agents don’t just follow rules; they understand context, trigger the right actions, and deliver consistent outcomes across sales, service, and operations.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to create an AI agent using Flow, step by step, without touching a single line of code. Whether you’re an admin, consultant, or someone exploring the future of automation, this walkthrough will help you build smarter, scalable AI experiences right inside Salesforce.
Table of Contents
What is an AI Agent?
An AI Agent in Salesforce is an intelligent digital teammate that uses Einstein AI, Flow, Apex, and Agentforce to understand natural language, interpret context, and perform tasks across the CRM. Unlike rule-based automations, it can analyze real-time data and perform tasks through various channels such as chat, email, or voice. They work securely within your org’s model and can handle activities such as qualifying leads, resolving cases, updating records, and generating proposals, bringing smarter, faster, and more proactive automation to Salesforce.
Why Build an Agent with Flow?
Flow is the ideal foundation for building AI Agents in Salesforce because it lets teams create smart, reusable, and no-code automations that an agent can easily execute. With drag-and-drop design, Flow supports everything from data updates to multi-step business processes, giving the agent both the “hands” and “brain” to act intelligently. Its secure, scalable, and low-maintenance approach makes automation accessible to admins, consultants, and non-developers while reducing technical debt for developers. Combining Flow with Agentforce enables efficient, governed, and scalable AI-driven automation across the business.
Setup Guide: How to Create an AI Agent Using Flow
Step 1: Purpose of creating the Agent
Before creating an agent, one question that should come to anyone’s mind is, What will this agent do? What specific problem should this agent solve? Will it guide customers through creating a case, share updates on an existing case, or support another business process? Having a clear, outcome-driven purpose ensures your agent is focused, useful, and aligned with real business needs. When you know exactly what task the agent should perform, you can design its actions, data requirements, and flow logic more effectively, creating an AI teammate that delivers meaningful value from day one.
Purpose: We want to create an agent to create cases and help them with the information about their case
Step 2: Org Setup
- Log in to the org
- Click on the gear icon in the right corner.
- Click on Setup
- Click on the Quick Search box, which is in the left corner, and type Agent.
- Click on Einstein Generative AI
- Select Einstein Setup
- Enable “Turn on Einstein.”
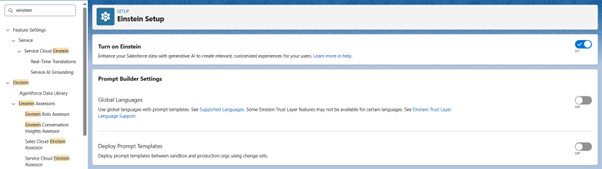
- Refresh the tab
- Click on the Quick Search box, which is in the left corner, and type Agentforce.
- Click on Agentforce Agent
- Enable the Agentforce by clicking on the “On” button in the right corner.
- Refresh the page
- Turn on “Enable the Agentforce (Default) Agent (It allows the user to use the default agent given by Salesforce)
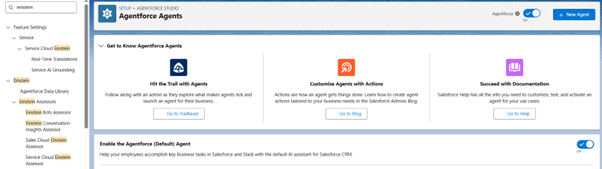
- Refresh the page
Step 3: Create a new agent
- Click New Agent on the Agentforce agent page in the right corner
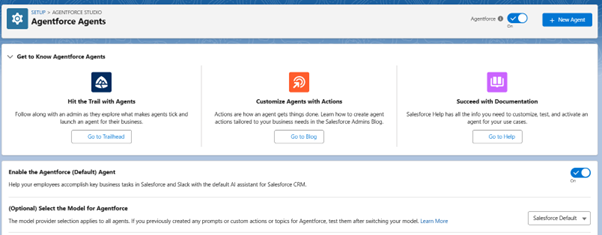
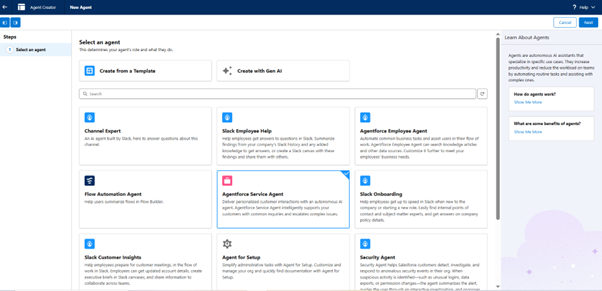
Step 4: Select an Agent
- Create from a Template: Salesforce has some pre-built templates, and the user can choose from them.
৹ Channel Expert: An agent designed to not only answer channel-specific inquiries but also guide users in the context of the Slack or communication space in which they find themselves.
৹ Slack Employee Help: An AI assistant that allows employees to quickly get an answer from Slack history, knowledge bases, and internal documentation.
৹ Agentforce Employee Agent: An internal helpdesk agent that automates tedious steps and provides knowledge to support employees across business functions.
৹ Flow Automation Agent: An agent that summarizes automations and interacts with Flow Builder automations to simplify troubleshooting and understanding of complex flows.
৹ Agentforce Service Agent: A customer-support agent built to manage common customer inquiries, troubleshoot issues, and escalate difficult cases for you as needed.
৹ Slack Onboarding: An agent that guides new employees in the onboarding process by retrieving key company information, contacts, and policies through Slack.
৹ Slack Customer Insights: An insights-driven agent that prepares employees for customer meetings by pulling account details and updates in Slack.
৹ Agent for Setup: A Salesforce admin assistant that allows you to configure, customize, and manage your org by using commands in natural language.
৹ Security Agent: An intelligent security assistant that monitors for unusual activity, explains risk, and provides remediation steps in Salesforce.
৹ Guided Shopping for B2C Storefronts: A shopping assistant that creates a guided conversation to help online shoppers find products, evaluate options, and complete orders.
৹ Agentforce for Guided Shopping – B2C: An AI agent that assists customers with frequently asked questions about products and orders, enhancing the shopping and checkout experience.
৹ Knowledge Space Agent: An agent that queries relevant data sources and provides concise summaries generated by AI for knowledge-based questions. - Create with Gen AI: It uses Salesforce’s AI to auto-generate an agent based on the description provided by the user.
- Select the template that suits your option, like Agentforce Service Agent, which we are choosing.
- Click on Next in the right Corner of the page.
Step 5: Select Options
- All options are pre-selected. To remove any option, click on it, and that option will be removed.
- Click on Next
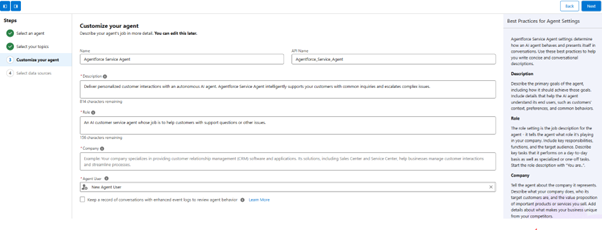
Step 6: Customize your agent
- Fill in the Name, API name, description, role, company, and agent user.
- Click on Next
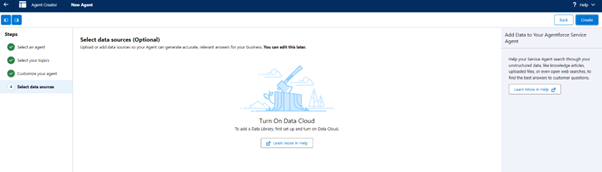
Step 7: Data Source
- Select the data source (If the agent needs to use Data 360, then we enable it)
- Click Create
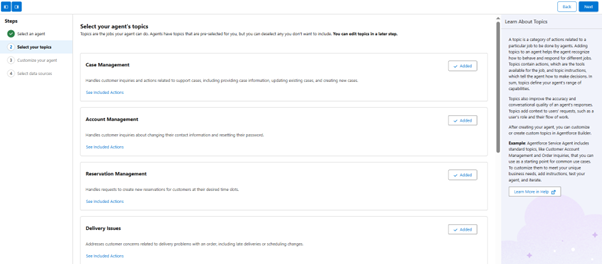
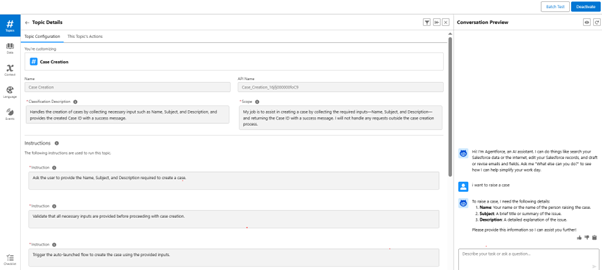
Step 8: Topic Details Selection
- Click on NEW
- Click on New Topic
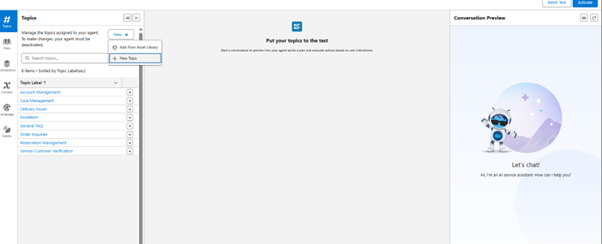
- Fill in the description of the topic, like “I want to create the topic for case creation.”
- Click Next
Step 9: Fill in the topic description
- Fill the required fields like name, API name, classification description, Scope, and Instruction (Salesforce fills the fields according to the description of topics, and it adds the instructions)
- Click next
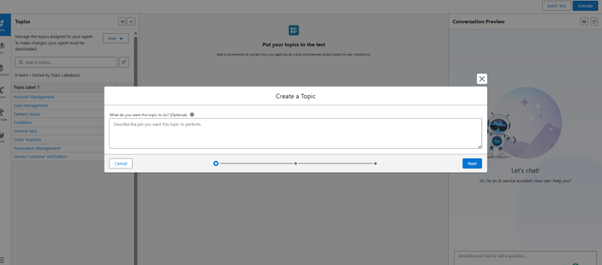
Step 10: Actions Selection
- Choose an action from the pre-built options, but do not select an action for case creation.
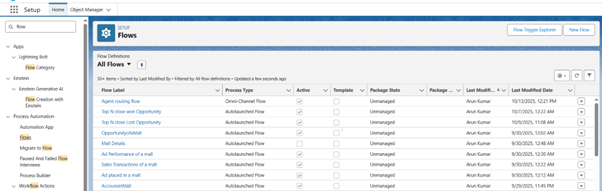
Step 11: Add Flow Action
- Click on Gear Option
- Click on setup
- Select Quick Search and type flow.
- Select New Flow
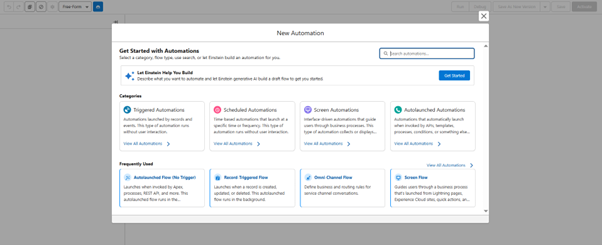
- Select Autolaunch flow
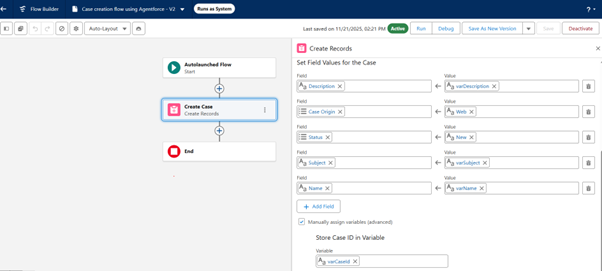
- Create the required flow to fill both the input and output variables that will be required
Step 12: Create an Agent action
- Select “This Topic action.”
- Click on New
- Select “Create New Action.”
- Select Flow
- Select the required flow for the case creation
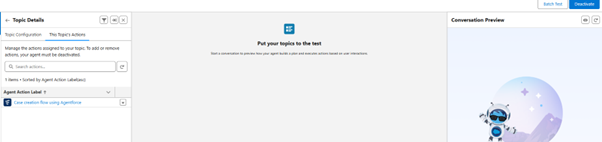
Step 13: Set the Instruction for action
- Set the required input that the user has to provide, like name, reason and description, and more.
- Set the required output that the agent will provide, like a case number.
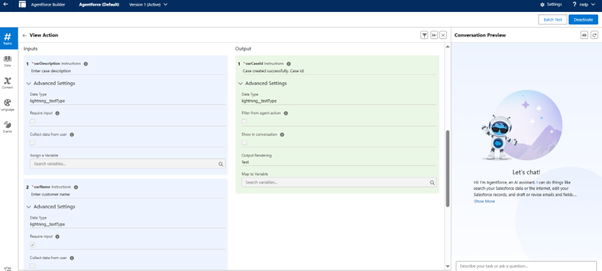
Step 14: Check the Permission Set of the flow
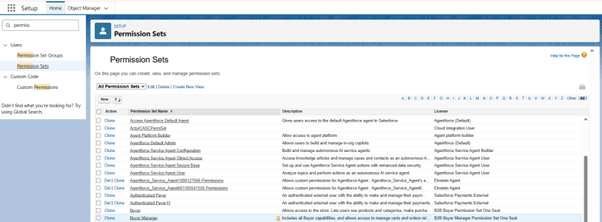
- Click on the Gear Icon
- Select Setup
- Search in the Quick Search box, type permission Set.
- Select Permission Set
- Click to clone a permission set
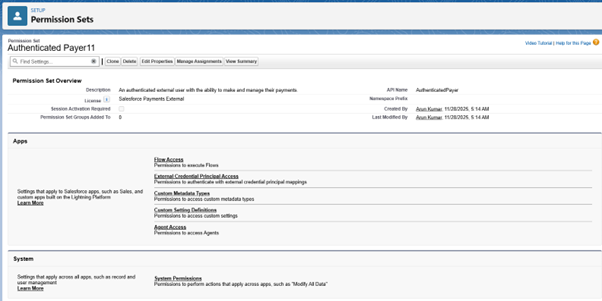
- Fill the Label, API Name, Description, and more
- Click Save
- Select Flow Access and provide the required permission to the flow.
Step 15: Test the Agent
- Type different inputs of the agent that the user can give, and see the output the agent will provide.
- Activate the agent
Conclusion
Building an AI Agent with Flow and Agentforce gives Salesforce teams a powerful, no-code way to introduce intelligent automation into their org. Flow provides the structured automation foundation, while Agentforce adds reasoning and natural language capabilities—working together like a digital teammate that follows business rules and completes tasks accurately. This approach keeps solutions scalable, secure, and easy for admins to maintain, making it a practical first step toward a smarter, faster, and more connected Salesforce experience.
Most Reads:
- How to Build a Clean Apex Trigger Framework: Step-by-Step Guide
- Build a Dynamic, Reusable Lightning Datatable in Salesforce LWC (With Metadata-Driven Columns, Search & Pagination)
- Beyond Triggers: The Apex Developer’s New Job in the Age of AI
- Agentforce Explained: The New Era of AI Agents Inside Salesforce
- Salesforce Marketing Cloud to Agentforce: The Future of Marketing Automation
- How to Create a WhatsApp Business Channel and Configure It in Meta Business Suite
Resources
- [Salesforce Developer]- (Join Now)
- [Salesforce Success Community] (https://success.salesforce.com/)
For more insights, trends, and news related to Salesforce, stay tuned with Salesforce Trail
- Akanksha Shukla#molongui-disabled-link
- Akanksha Shukla#molongui-disabled-link
- Akanksha Shukla#molongui-disabled-link
- Akanksha Shukla#molongui-disabled-link













